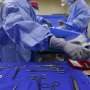
Older adults with serious illness before surgery use far more health care resources after surgery
- medicalxpress.com language
- 2025-07-24 22:54 event
- 3 months ago schedule

Domain EYEION.com for sale! This premium domain is available now at Kadomain.com

Konstanz researchers identify an enzyme that plays a role in the migration of cells in our body—not only during normal tissue formation and wound healing, but also when tumor cells metastasize. This makes the enzyme an interesting candidate for potential future therapeutic approaches.
During a severe heart attack many heart muscle cells die and are replaced by scar tissue to stabilize the heart wall. Connective tissue cells, known as fibroblasts (FB), are the dominant cell type in scar tissue.
Mizzou scientist discovers how a deadly bacterium spread by the lone star tick survives, bringing hope for new treatments.
It seemed like a simple idea. Design a device that will make it possible for a human eye to remain alive and functional outside of the body. At least for a few hours. And then a few days.
Dana-Farber research uncovered the potential for underdiagnosis of this aggressive cancer and identified additional tests required for an accurate diagnosis.
Cannabis has gained increased use in the United States, outpacing alcohol as Americans' daily recreational drug of choice. Nearly 20% of cannabis users have admitted to driving after using the drug. However, unlike for alcohol, reliable roadside tests for cannabis don't exist. Even blood tests can't determine when a person used cannabis, leaving law enforcement without a way to determine a person's recent use, much less how intoxicated they are.
Are you a woman who exercises regularly? If so, here's a vital question: do you train your pelvic floor muscles as part of your routine?
In an unexpected twist in the fight against cancer, humble kitchen bacteria and a plant best known for sweetening tea could one day help in treating one of humanity's deadliest diseases, new research suggests.
Fetal exposure to inflammation has long been identified as a risk factor for a range of harmful conditions, but new research suggests systemic inflammation alone is not enough to cause lung injury.
Older adults who have serious illness before undergoing elective surgery had hospital stays twice as long as similarly aged counterparts; were twice as likely to return to the hospital or the emergency department; and had almost double the yearly costs of health care, according to a study published in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
As artificial intelligence is rapidly developing and becoming a growing presence in health care communication, a new study addresses a concern that large language models (LLMs) can reinforce harmful stereotypes by using stigmatizing language. The study from researchers at Mass General Brigham found that more than 35% of responses in answers related to alcohol- and substance use-related conditions contained stigmatizing language. But the researchers also highlight that targeted prompts can be used to substantially reduce stigmatizing language in the LLMs' answers. Results are published in The Journal of Addiction Medicine.
Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that affects thoughts, moods, perceptions, and behaviors. Affected individuals experience positive symptoms like delusions and hallucinations, and negative symptoms like social withdrawal, cognitive deficits, disorganized thoughts and speech, and a decreased experience of pleasure. While schizophrenia is caused by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, precise mechanisms remain elusive.
New research from investigators at Mass General Brigham suggests that a commonly used type 2 diabetes medication is linked to a higher rate of heart-related conditions compared to medications that hit other targets. The study examined nationwide data from nearly 50,000 patients treated with different sulfonylureas and found that glipizide—the most widely used drug in the U.S. within this category—was linked to higher incidence of heart failure, related hospitalization and death compared to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Results are published in JAMA Network Open.
Cancer cells and tumors do not exist in a vacuum. Far from the isolation and self-sufficiency of the fictional Wakanda, tumors develop in and alter the nearby milieu of immune cells, connective tissue, blood vessels and a sea of proteins and carbohydrates that provide structure and other supportive functions.
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting are among the most distressing side effects of anti-cancer treatment, particularly for those receiving highly emetogenic regimens such as anthracycline plus cyclophosphamide combinations. This major side effect compromises a patient's quality of life and willingness to continue therapy. Therefore, there is a crucial need to devise an effective antiemetic management approach for optimizing cancer care and patient well-being.
More women at higher risk of breast cancer should be offered a mastectomy, according to researchers at Queen Mary and London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
Oxidative stress is considered to contribute to the development of cancer. However, a recent study in Japan showed that oxidative stress may suppress rather than cause cancer development in individuals with variants of the BRCA2 gene. This finding was published in Redox Biology.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), a powerful form of immunotherapy, have revolutionized cancer treatment by unleashing the body's own immune system to fight tumors. These compounds target the programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), a surface protein typically found on tumor cells, which enables the tumors to avoid recognition by immune T cells.
Use of billing codes in big data sets to find diagnoses can result in up to two-thirds of cases being mistakenly identified, new UCLA-led research finds.